Communities lower cost of living with Open Access Internet fiber innerducts
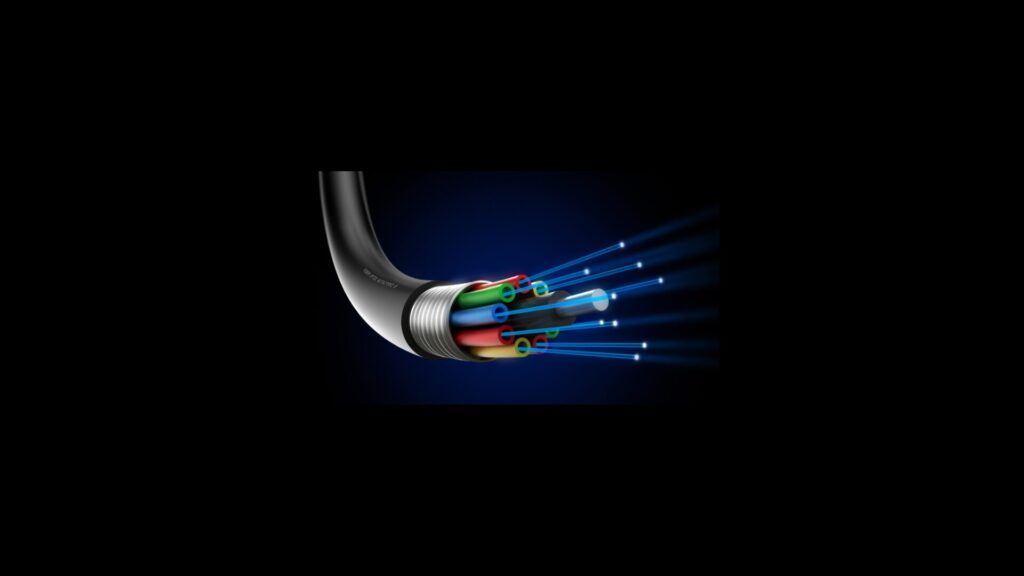
Understanding and leveraging fiber innerducts in community broadband networks can have a significant and positive impact on the cost of living and housing affordability in several ways. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how this works:
What Are Fiber Innerducts?
Fiber innerducts are sub-duct systems installed within existing conduit systems to provide multiple, segregated pathways for fiber optic cables. These innerducts protect and manage optical fibers which are crucial for high-speed internet connections. By using innerducts, communities can maximize the use of existing conduit infrastructure, efficiently manage space within the conduits, and simplify future upgrades or maintenance of fiber networks.

The concept of open access internet is intricately linked to the strategic use of fiber innerducts within community broadband initiatives. Open access internet refers to a model where the physical network infrastructure, including fiber optic cables and associated facilities, is separated from the services provided over the network. This means that the infrastructure is open for use by multiple service providers under equal terms and conditions, promoting competition and improving service quality. Here’s how the strategic use of fiber innerducts supports and enhances the open access internet model:
Understanding Open Access Internet and Fiber Innerducts
- Open Access Internet Model:
- Infrastructure Sharing: In an open access model, the physical broadband infrastructure (like fiber cables) is accessible to multiple ISPs and other service providers. This separation of infrastructure and service provision ensures that no single provider has a monopoly over the network, fostering a competitive environment that can lead to lower prices and higher quality services for consumers.
- Promotes Competition: By allowing various service providers to use the same infrastructure, the open access model encourages healthy competition, as providers compete on service quality, customer service, and price rather than infrastructure ownership.
- Enhances Service Diversity: Consumers can choose from a variety of services and providers, which encourages innovation and diversification in the types of services offered, including specialized services for businesses, high-quality residential services, and affordable options for low-income households.
- Fiber Innerducts in Broadband Networks:
- Efficient Use of Conduit Space: Fiber innerducts are sub-duct systems that enable multiple fiber cables to be run within a single conduit, maximizing the use of space and allowing for better management and protection of the fibers.
- Simplifies Upgrades and Maintenance: Using innerducts makes it easier to install additional fibers as demand grows or technology evolves, without the need for new conduit infrastructure. This supports the scalability and flexibility essential in an open access network.
- Cost-Effective Network Expansion: By using innerducts, the cost and disruption of expanding network capacity are significantly reduced, making it economically viable to enhance and grow the network over time without substantial new investments in trenching and conduit laying.
Strategic Benefits of Fiber Innerducts in Open Access Models
- Enabling Multiple Providers:
- Fiber innerducts allow the physical infrastructure to be shared among multiple service providers without interference. Each provider can have their own dedicated set of fibers within a common conduit, facilitated by innerducts, ensuring that they can operate independently and securely.
- This capability is central to the open access model, as it physically separates the services provided by different entities but within the same infrastructure, aligning perfectly with the philosophy of open access.
- Reducing Costs and Barriers to Entry:
- The use of innerducts lowers the initial costs for ISPs wanting to enter the market because they don’t need to invest heavily in infrastructure. Instead, they can lease fiber capacity within existing innerducts, dramatically reducing the barrier to entry and encouraging more providers to offer services.
- This can lead to more competitive pricing and better service offerings for consumers, as the savings on infrastructure are often passed down to customers.
- Facilitating Future-Proof and Scalable Networks:
- Innerducts provide a way to future-proof broadband infrastructure by making it easier to pull through new fibers as needed. This is particularly important in open access networks, where the ability to quickly and efficiently upgrade services in response to changing technologies and customer demands is critical.
- This scalability supports the dynamic nature of open access networks, where new providers may come and go, and service needs may evolve rapidly.
- Promoting Equitable Access to Broadband:
- By supporting a variety of service providers, open access networks can serve a wider range of communities and demographics, including underserved and rural areas often ignored by major ISPs due to cost and demand constraints.
- Fiber innerducts contribute to this by making it more cost-effective to extend services to these areas, as multiple providers can share the cost of extending the physical network.
- Enhancing Network Reliability and Service Quality:
- With multiple providers using the same infrastructure, there is a natural drive to maintain high network reliability and quality—providers need to ensure their segment of the network is robust to remain competitive.
- The protective environment of innerducts enhances the overall reliability of the fiber network, reducing downtime and maintenance costs, which contributes to higher service standards across the board.
Real-World Applications and Implications
- Municipal Networks: Cities like Chattanooga, Tennessee, have utilized open access models alongside strategic innerduct systems to create a municipal network that serves as a backbone for various ISPs to deliver competitive services to residents and businesses.
- Rural Broadband Initiatives: In places like Orangeburg County, South Carolina, the use of fiber innerducts in an open access framework has enabled the expansion of broadband to rural and underserved areas, fostering equitable digital access and supporting local economies.
- Innovative Projects: Networks like Utah’s UTOPIA and Colorado’s EAGLE-Net have demonstrated how open access, supported by efficient innerduct systems, can facilitate a range of services from different providers, boosting local innovation and consumer choice.
Conclusion
The strategic use of fiber innerducts is pivotal in realizing the full potential of open access internet models. By facilitating infrastructure sharing, reducing costs, enhancing service quality, and promoting equitable access, innerducts support a competitive and diverse broadband marketplace. This approach not only leads to better consumer outcomes but also supports broader goals of digital inclusion and economic development, making it a key strategy in the quest for universal and affordable broadband access.





Responses